VW bus spark plugs service
... for Type 1 and Type 4 engines (1968-1979)
Service and specifications

| A | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect every | 10,000 km (6,000 mi) |
From "So wird's gemacht" manual: - Inspect: 10K km - Replace: 20K km |
| Replace every | 24,000 km (15,000 mi) | The FI engine originally used long-life spark plugs. If NGK plugs are used, their replacement interval is 30,000 mi. (48,000 km). |
| Type | NGK B5ES NGK B5HS |
Type 4 engine Type 1 engine Modern replacement for originally recommended spark plugs in the Owner's Manual (see appendix for reference). Part number codes: B: 14 mm thread 5: heat range (lower is hotter) E: 19 mm thread reach / H: 12.7 mm thread reach S: copper core center electrode. Trivalent metal plating on the threadprovides anti-corrosion and anti-seizing properties. Longevity: 30,000 mi. (48,000 km). Other than old stock, only the BR5ES (with 5 kOhm resistor) type is currently available |
| Air gap | 0.7 mm (0.028") 0.6 mm (0.024") |
Fuel injection engine (Type 4) Carbureted engines (Type 1, Type 4) |
| Torque | 30 N·m (22 lb·ft) | NGK recommends 18-21.6 lb·ft (25-30 N·m) for aluminum heads. There is also a spark plug torque discussion at The Samba forum. |
| Thread size | M14 x 1.25 x 20.8 mm | Diameter x pitch x hexagon size. |
| Thread reach | 19 mm | |
| Hex socket size | 21 mm |
Installation tips
- 👉 Do the removal and installation with a cold engine. Metal expands when it's hot. The aluminium heads expand more than the spark plug when heated up, with the consequence that the spark plug can be fastened in place.
- 👉 Clean up the spark plug holes before installation. You don't want to torque against dirt or debris.
- 👉 Finger tight the sparkplugs first, then use a torque wrench set at the specified torque.
- 💡 Your fingers won't reach to the spark plug sockets where the engine tin covering them is higher. You can use a small section of fuel hose plugged into the spark plug's terminal end snuggly. Then do the installation from the rubber hose with longer reach.
- 💡 Consider removing only one spark plug wire at a time. That way there is no chance of possibly getting the spark plug wires mixed up.
- 💡 The firing order for all air-cooled Volkswagen engines is 1-4-3-2, so make sure the plug wires go around the distributor cap clockwise in that order.
- 💡 You should use a torque wrench for installation. Consider investing in one if you don't have it, or borrowing it from someone. If you are intending to continue servicing your bus yourself, you'll be using it for many other maintenance procedures. In a pinch, if you are in a situation where a torque wrench is not available, you can install the spark plugs finger tight and then add another quarter turn (90°) with a hex wrench.
FAQ
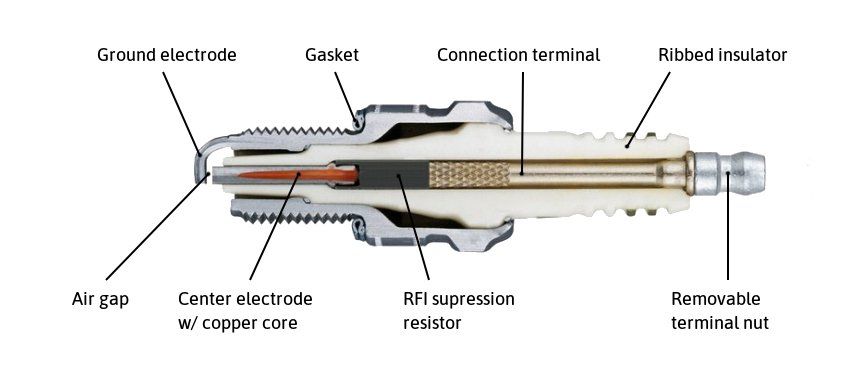
Should I use a spark plug with RFI suppression resistor?
ℹ️ VW busses with stock ignition do not need spark plugs with integrated resistor.
This is because the ignition circuit already contains the additional resistance: the rotor cap has 5 kΩ resistor, and each spark plug connector has an integral 1 kΩ resistor. That said, resistor spark plugs can be used (see more below).
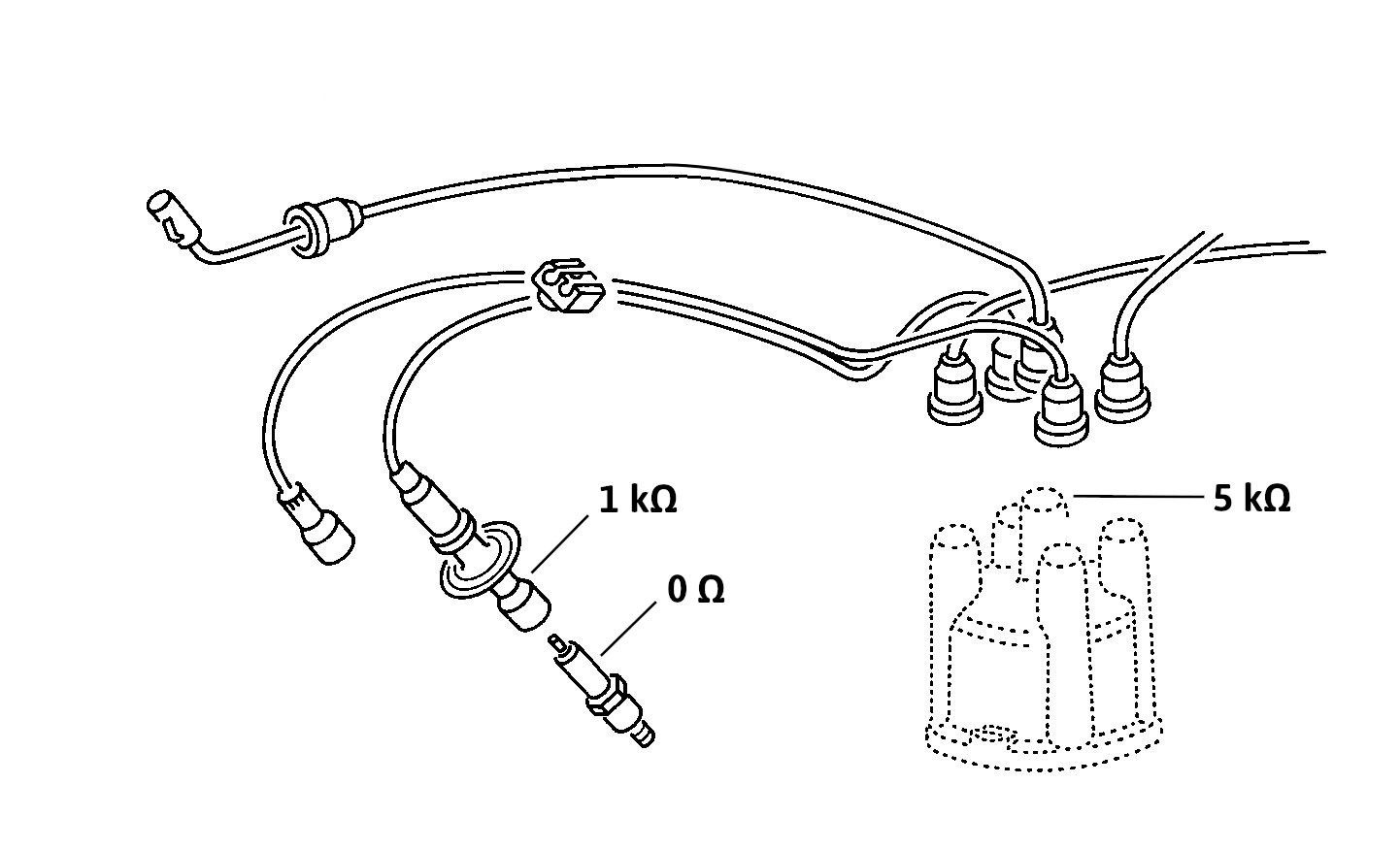
Early fuel injector systems were designed to use resistor spark plugs to reduce radio frequency interference (RFI) that could affect sensitive electronic systems, such as ECUs. The effect of the resistor is to attenuate the spark's energy and thus minimize RFI. Not all vehicles featured the integral resistance in the ignition wiring as the Type 2 bus.
At the time of writing (2017), spark plug manufacturers have phased out non-resistor spark plugs and only the resistor type is available. Non-resistor spark plugs are still available from old stock, though. So if you want to be close to stock, the non-resistor option is still that option available.
That said, the additional resistance added by the spark plug resistor (generally 5 kΩ) is probably not critical. The extra resistance on the circuit affects the spark line section of the secondary circuit's voltage waveform by varying its slope.
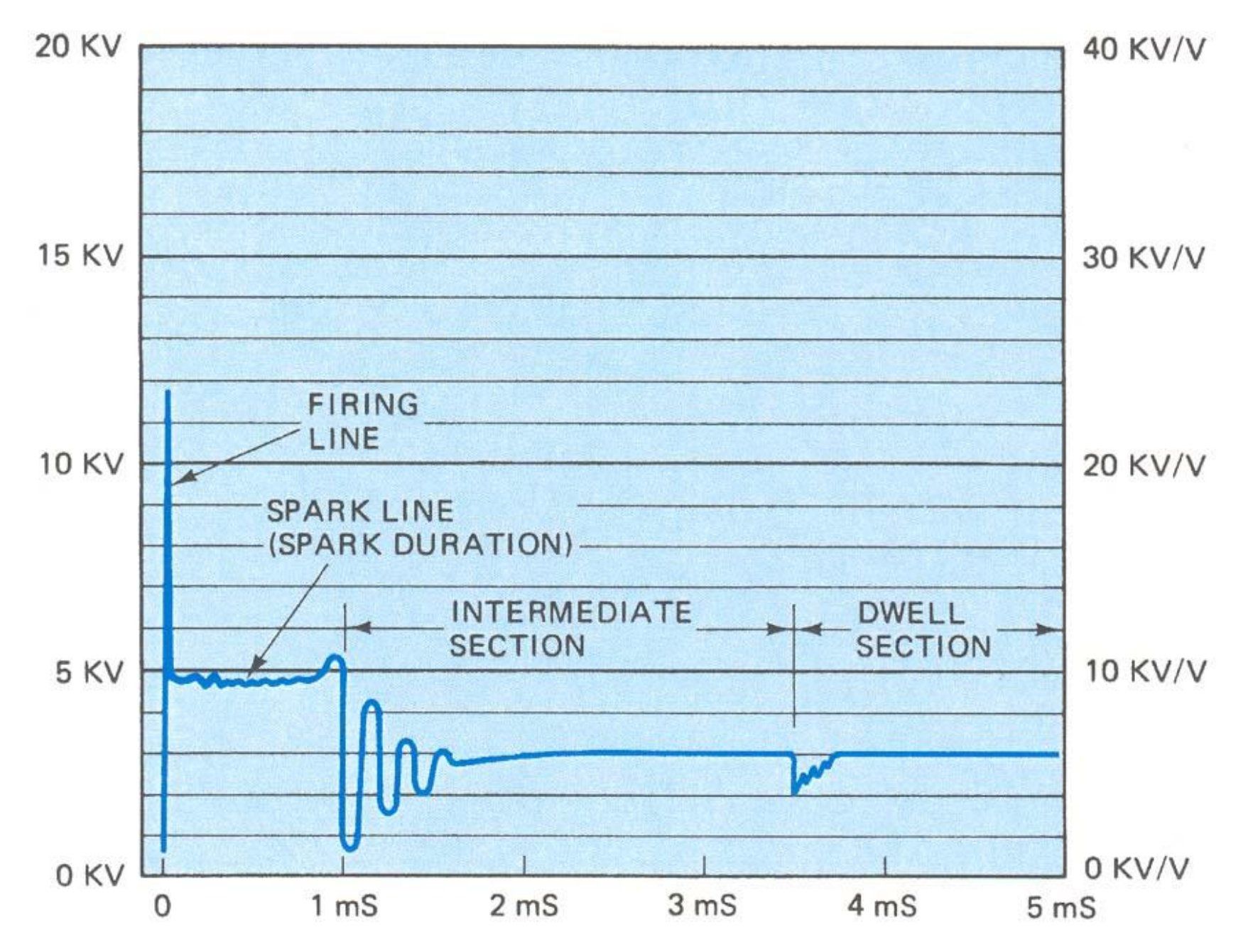
According to this source, as long as a value of 20 kΩ is not exceeded:
Spark or burn section (spark duration): the amount by which this line slopes away from the horizontal is directly related to resistance in the plug and coil HT leads (ignition supression). [...] The total resistance between the centre terminal of the coil and the centre electrode of the plug should not exceed about 20 kΩ [...] Actual resistance is not critical but anything more than 30 kΩ may cause problems.
Testing your ignition with an oscilloscope, Electronics Today International, February 1977
Richard Atwell performed and documented some tests with varying rotor cap resistance as well. As it's a series circuit, the results can be extrapolated to be similar for varying spark plug resistance. The result was that with an increased resistance (up to the stock 5 kΩ of the rotor cap) a more optimal waveform was generated.
Understanding the ignition system, Richard Atwell (scroll down to the "Which rotor" section for the results)
Finally, to conclude that resistor plugs can be used nevertheless in VW busses, here is a quote from Bosch's spark plug documentation:
Resistor spark plugs can be fitted in non-resistor applications. Bosch recommends fitting a resistor type spark plug for every application.
Can I reuse the crushable gasket when reinstalling my spark plugs?
ℹ️ Plug manufacturers recommend the use of a new gasket any time a plug is reinstalled after inspection or cleaning.
You can purchase inexpensive 14 mm gaskets such as these:

That said, many bus owners have reinstalled spark plugs without replacing the gaskets over the years, so in a pinch, you can also do the same.
With terminal nut?
ℹ️ Use spark plugs with a threaded terminal stud. They are generally sold with a removable terminal nut that can be detached before installation.
The terminal is connected to the ignition lead connector via a small clip that pushes against the terminal stud's thread.
More on spark plug terminal types
Regular, extended or recessed center electrode tip?
ℹ️ Spark plugs for the Type 2 use a regular center electrode tip, raising 1 mm from the thread.
More on spark plug center electrode designs
Which heat range?
ℹ️ Spark plugs for the Type 2 are on the hotter heat range end (e.g. heat range code 8 for Bosch, or code 5 for NGK).
Should I use anti-seize to prevent galling of the threads?
Sparingly apply anti-seize compound to the upper two thirds of the threads to lubricate them. Don't get any anti-seize on the plug electrode or it will foul
(Tom Wilson on How to Rebuild Your Volkswagen Air-Cooled Engine, pp138)
Plug manufacturers do not recommend the use of anti-seize, though, as it modifies the torque specifications. If anti-seize is used, they suggest reducing the torque values by 20 - 40 %.
Appendix: historical plug type cross-reference
Fuel injection engine
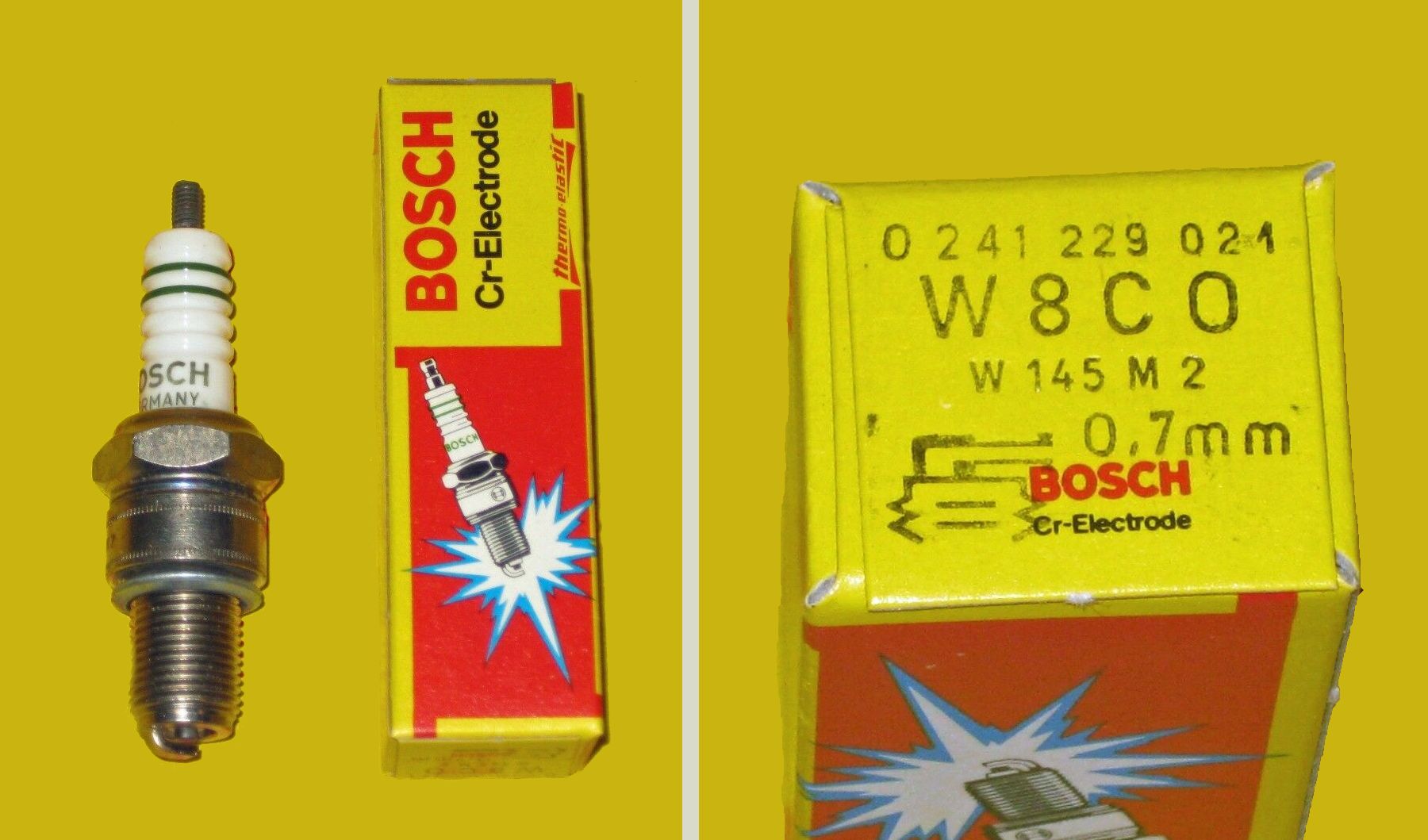
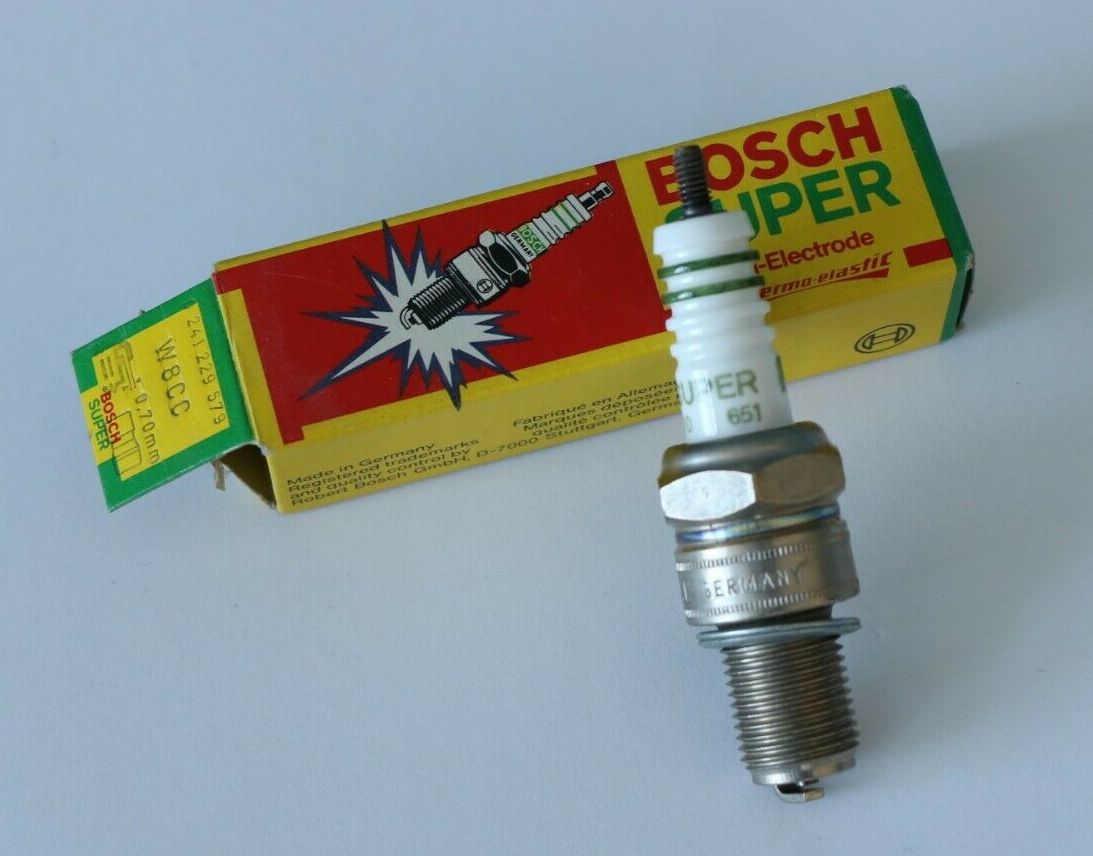


From type2.com's spark plug reference charts:
| Brand | # in Bentley | Alternate # |
|---|---|---|
| Beru | 145/14/3L | - |
| Bosch | W145M2 W8C0 [0 241 229 021] | W8CC0 [??] W8CC [0 241 229 579] W7 DTC [0 241 235 643] WR 8 AC [0 242 229 534] WR 7 DP [0 242 235 541] WR 7 D+ [0 242 235 909, -946, -663] |
| Champion | N288 or N5C (replaced N288) | N11YC |
| NGK | - | B5ES or BR5ES (resistor) |
From "Reparaturleitfaden" Aug. '81 (V.A.G):
| Type/Engine/Feature | under 25°C | over 25°C |
|---|---|---|
| 2/2.0 l/L-Jetronic | Bosch W8CO Beru 145/14/3 L Champion N288 |
Bosch W8C0 Beru 145/14/3 L Champion N288 |
ℹ️ The original Bosch part number was W 145 M2 / W8C0. The newer part number was W8CC0. It was reportedly a long life version of the W8CC, with reinforced electrodes. Insted of having ~2.5mm electrodes, the W8CC0 had ticker (ca. 3.0 mm) electrodes, so that the gap erosion was slower.
ℹ️ Bentley shows Bosch W 145 T2 (0 241 229 548). The latest designation by Bosch is W8CC (0 241 229 579). Stock gap is 0.024 inch, 0.60 mm.
Dual carburetor engine
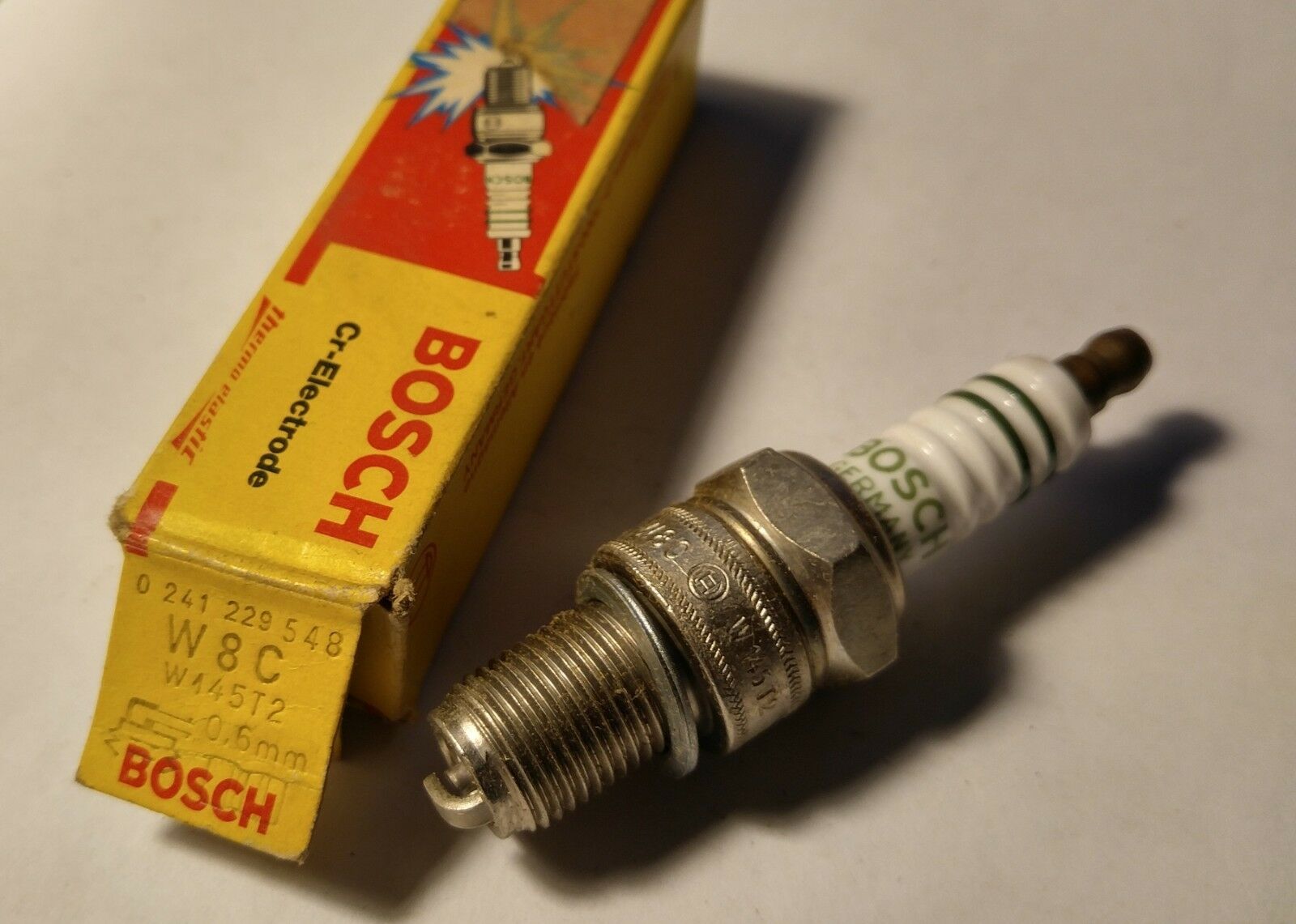

All engines
| Source | Engine | Conditions | Beru | Bosch | Champion | NGK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haynes | 1.7L-1.8L carbs | Normal | 14-8 C |
W8C |
N. 88 | - |
| Haynes | 1.7L-1.8L carbs | Tropics | 175/14/3 | W 175 T2 | - | - |
| Haynes | 1.8L-2.0L FI | N/A | 145/14/3L | W 145 M2 | N 288 | - |
| '79 owner's manual (US) | 2.0L FI | N/A | 145/14/3L | W 145 M2 | N-288 | - |
| '79 owner's manual (DE/UK) | 1.6L carbs | Normal | 145/14/14-8a | W 145 T1·1 / W8a | L88A | - |
| '79 owner's manual (DE/UK) | 1.6L carbs | Heavy duty above 25°C | 175/14 | W 145 T1 | - | - |
| '79 owner's manual (DE/UK) | 2.0L carbs | Normal | 145/14/3/14-8c | W 145 T2/W8C | N7 | - |
| Bosch (2017) | 2.0L FI | N/A | - | W 8 AC | - | B5HS |
| Bosch (2017) | 2.0L FI | N/A | - | W 7 DP | - | BP6ES |
| Bosch (2017) | 2.0L FI | N/A | - | W 7 D+ | - | BP6ES |
From Reparaturleitfaden, Aug. '81
| Engine | Fuel delivery | Normal conditions (< 25°C) | Heavy duty (> 25°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3L-1.6L | Carbs | Bosch W 8 A Beru 14-8 A Champion L 88 A |
Bosch W 7 A Beru 14-7A |
| 1.7L-1.8L-2.0L | Carbs | Bosch W 8 C Beru 14-8 C Champion N 7 |
Bosch W 7 C Beru 14-7 C |
| 2.0L | Injection | Bosch W 8 CO Beru 145/14/3 L Champion N 288 |
Bosch W 8 CO Beru 145/14/3 L Champion N 288 |